 |
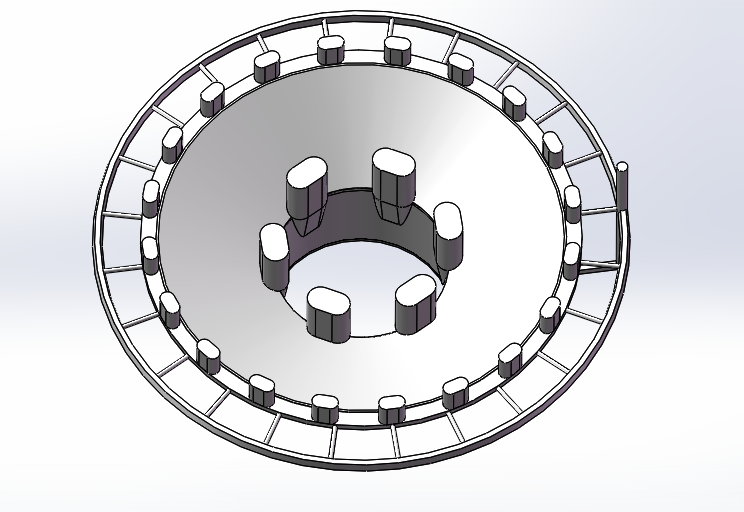 |
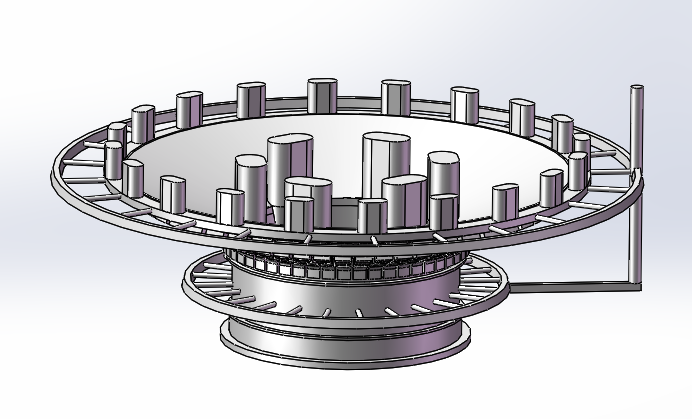
1.Casting Technology Design of Grinding Mill Head -1
|
2.Casting Technology Design of Grinding Mill Head -2 |
 |
 |
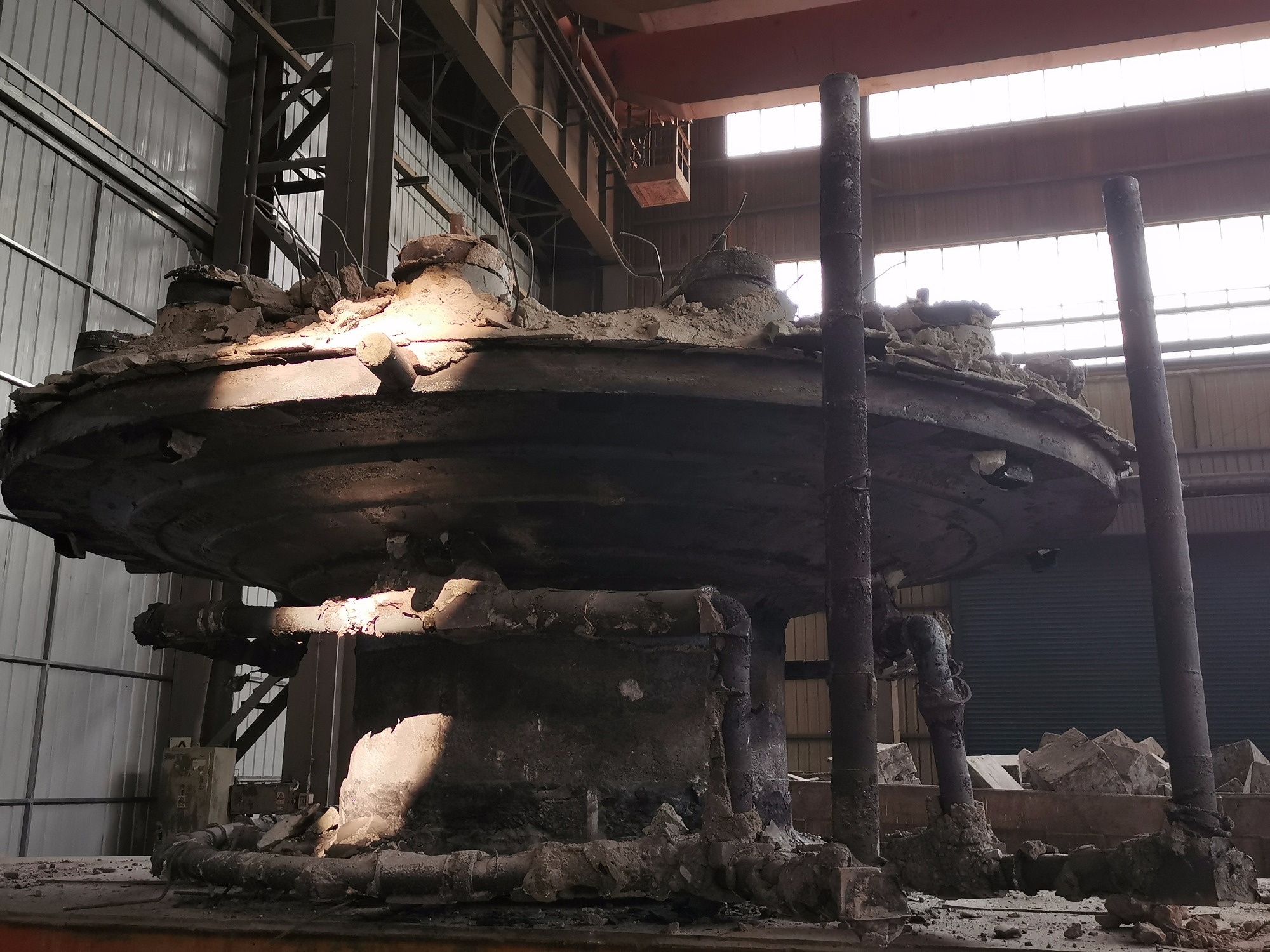
| 3.Roughcast of Grinding Mill-1 |
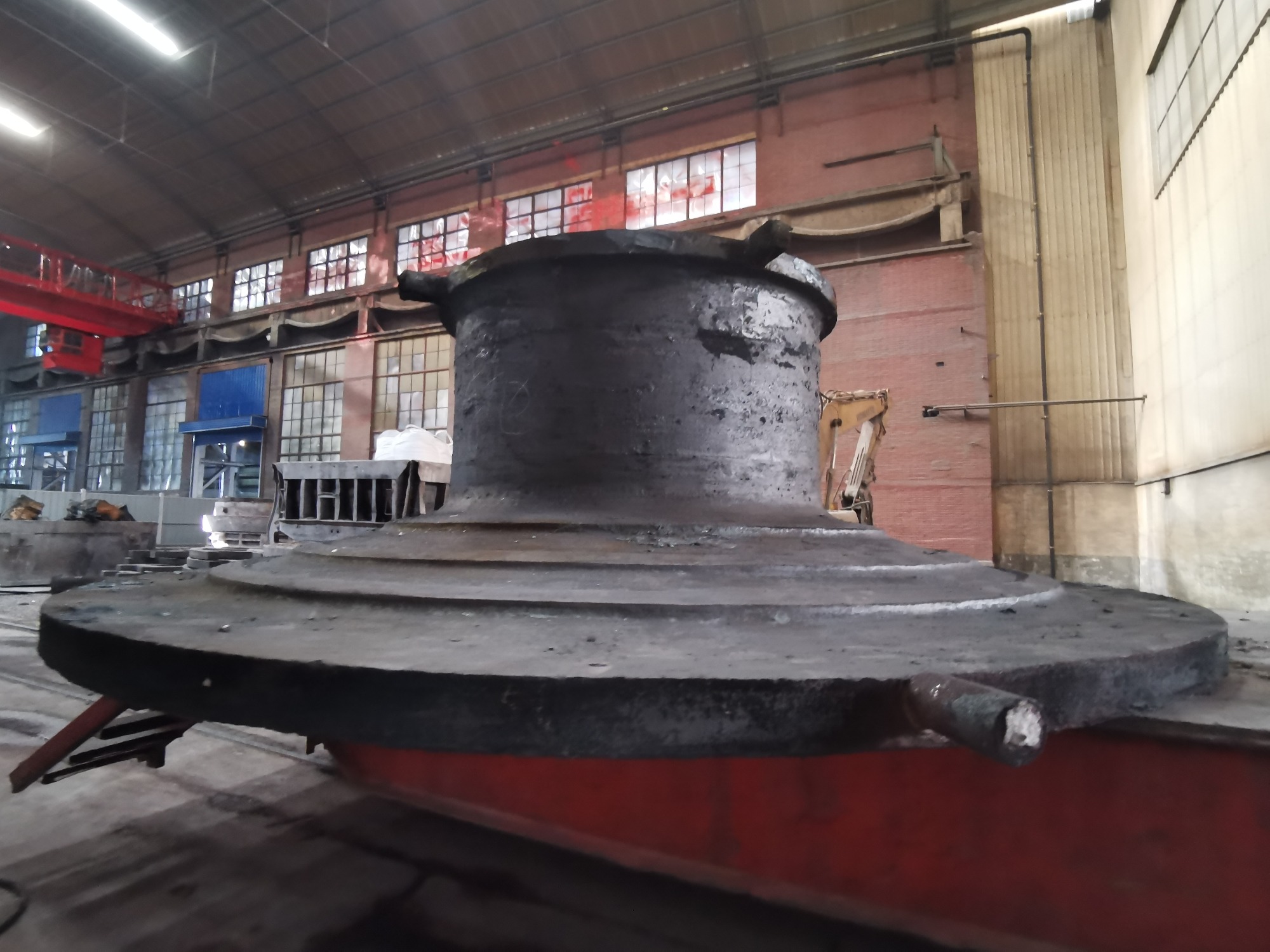
4.Roughcast of Grinding Mill-2 |
■ Grinding Mill Head casting process
Grinding Mill Head R zone refers to the corner of the transition part between the journal and cone, is the key force position, the quality requirements are particularly stringent. The main defects in R zone of Grinding Mill Head are shrinkage, porosity and crack. Defects are mostly buried under the skin of the arc transition zone of steel castings. After processing, some of them are exposed to the surface, and some of them are located at the center of the thickness of the workpiece in the arc zone, and most of them are parallel to the circumferential direction. The effective solution is to set up a full circle indirect external chiller thick enough in R area.
■ Grinding Mill Head smelting
strict process control measures are adopted in every process and node of smelting. Computer real-time tracking control is realized in the smelting process. Pipeline sampling + spectral analysis + gas analysis is used to detect the chemical element content. After meeting the requirements, it is transferred to the next process to effectively ensure that the chemical composition meets the standard requirements. During the whole refining process, argon is blown, and the oxidizability is required to be reduced to less than 7x10-6 before alloying. The inclusions are fully floated by spheroidizing with SiAl-Ca-Ba refining agent, and the soft blowing time before tapping is longer than 10 minutes. When pouring, argon blowing environmental protection pouring is adopted to reduce oxidation in pouring process. At the same time, argon blowing sliding plate is used to ensure automatic pouring during pouring, reduce the oxide caused by drainage into the cavity, and ensure the quality of castings.
■ Grinding Mill Head heat treatment process
The purpose of normalizing heat treatment is to fully dissolve precipitates in castings, form small grain austenite after austenitizing, and form fine F+P structure after cooling. After normalizing, a small amount of carbon in the structure is precipitated in the form of carbide by tempering at medium and high temperatures. At the same time, the residual stress of the castings is reduced and the dimensional stability of the later castings is guaranteed.




